Motion Through the First Cervical Vertebrae Is Best Described as
60 degreesof lateral bend. Cervical two is called the axis as it is the one essential for allowing rotation to occur in the cervical spine.

First Cervical Vertebra An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The motion of a segment is identified by the number of the vertebra above and the motion of this vertebra is always related to the subjacent one.
. The carotid-vertebral space is the surgical window between the carotid artery and the vertebral artery Fig. The first two cervical vertebrae called the atlas C1 and the axis C2 are unique even to the cervical region. The rest of the cervical vertebrae C3-C7 are considered typical and are described as.
Cervical flexion B ipsilateral lateral flexion U and contralateral rotation U 500. Cervical vertigo is best described as dizziness that occurs when you move your neck. An interspace is identified by the numbers of the two surrounding vertebrae for instance C45.
The atypical vertebrae are cervical level one and two C1 and C2. Watch Spinal Motion Segment. Atlas and axis respectively.
It reduces magnification of the cervical spine 2. The disc between the spinal bones is. Which of the following is the best explanation for why the lateral cervical spine projection needs to be performed with a 72-inch SID.
Cervical Fusion is a major surgery that involves joining one or more of the spinal bones together using screws bolts and plates 1. While there are different reasons for a person to. LIMITATIONS OF MOTION.
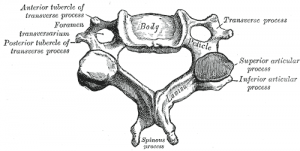
Both the atlas and axis are small flat vertebrae. The bodies of the typical vertebrae are. Fractures of the cervical spine can be described based on the level involved and typically divided into three groups.
This support structure at the atlanto-occipital and atlantoaxial joints includes the tectorial membrane and the atlantoaxial anterior and posterior alar and transverse ligaments. The facet apophyseal joint surfaces of most lumbar vertebrae are oriented largely in the frontal plane. What exactly is it.
Cervical one is also called the atlas as it supports the weight of your skull. The anterior approach to the spine first described by Robinson and Smith in their 1935 landmark paper is best employed when adequate decompression with removing a vertebral body is required. Cervical Fusion is often recommended when chronic neck pain problems worsen over time.
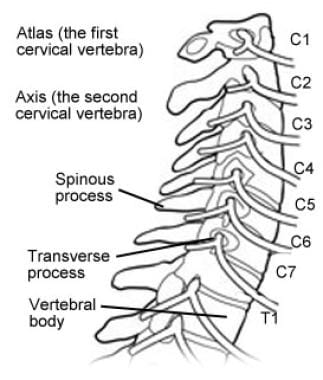
The hardware may be placed in the front anterior or the back posterior of the Cervical spine. The third through the sixth vertebrae C3-C6 are considered typical while the first C1 second C2 and seventh C7 are modified. C1 C2 and the sub-axial spine C3 to C7123 The cervical spine is a dynamic structure tasked with protecting nervous innervation to the entire body while also maintaining a range of motion for the head and neck.
A vascular watershed exists between the apex and the base of the odontoid. The cervical vertebrae are numbered in the conventional way C2-C7. It is a useful landmark for locating the lower cranial nerves X.
Typically nonsurgical treatments are tried first when treating pain stemming from the C2-C5 motion segments with the exception of those stemming from spinal cord compression as described above. These two segments work together to produce rotation lateral flexion flexion and extension of the head and neck. 50 degrees of flexionextension of cervical spine.
Limitation of motion in the first two cervical vertebrae is due to a ligamentous support system specific to this area of the spine. The first 2 C1 and C2 are highly specialized and are given unique names. See All About the C2-C5 Spinal Motion Segments.
The small ranges of motion between the 2 vertebrae can add up to significant ranges of motion for the entire cervical spine in terms of rotation forwardbackward and side bending. The seven cervical vertebrae are the smallest and most mobile of all vertebrae reflecting the wide range of motion available to the head and neck Fig. It results in better spatial resolution of the cervical vertebrae a.
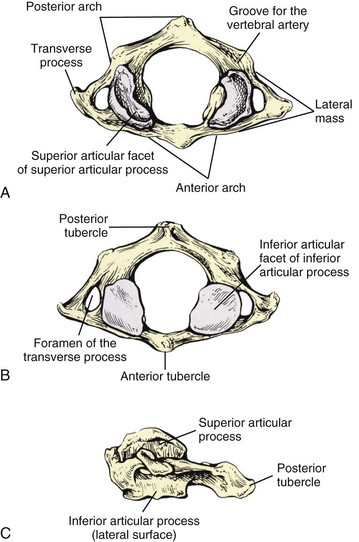
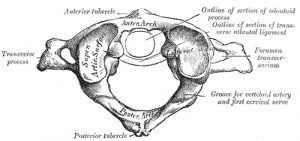
It is made up of 7 vertebrae. Has lateral masses which are connected by an anterior and posterior arch. It prevents size distortion of the cervical vertebrae 3.
First the alterations in position that each osseous unit ie skull base or cervical vertebrae experienced during airway manipulation were described independently of adjacent structures yielding a value for the absolute rotational movement of that object in space. 50 There is usually minor muscle splitting in this approach and so it is considered to be more favourable for patients post-operatively. 1 and 3 d.
50 degrees of rotation of cervical spine. It subdivides into five regions based on curvature and morphology. Fractures of the cervical spine are a.
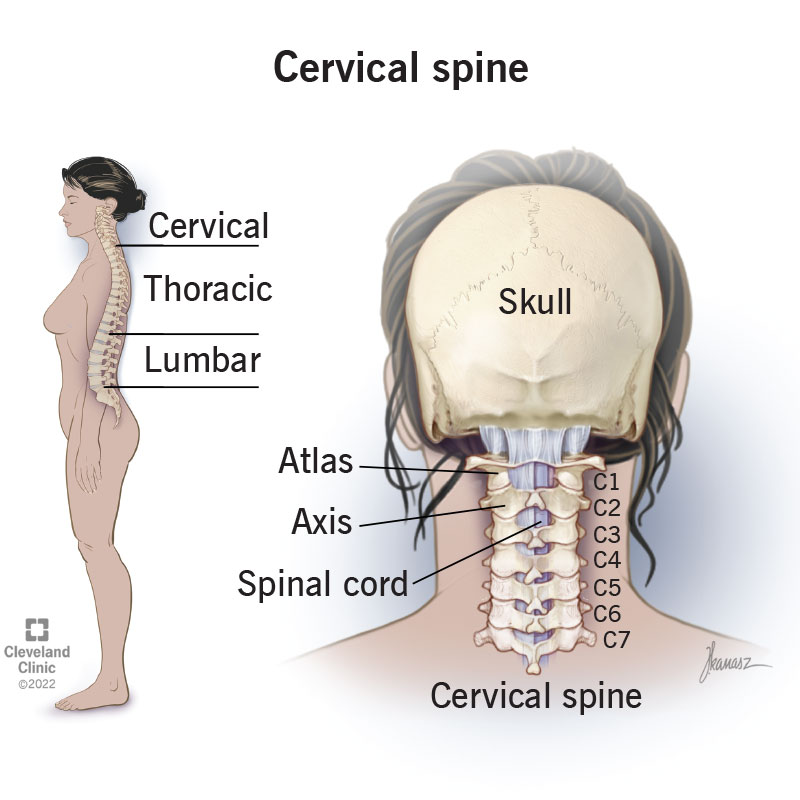
If pain persists despite 3 to 6 months of nonsurgical treatments or if numbness andor weakness continues to worsen surgery may be considered. Has no vertebral body and no spinous process. The spine or vertebral column is a segmental set of 33 bones and associated soft tissues that comprise the subcranial portion of the axial skeleton.
2 The transverse process of the first cervical vertebra is the most prominent of the vertebrae and is palpable deep to the superior attachment of the sternocleidomastoid muscle in patients who have a thin neck. The cervical thoracic and lumbar spine the sacrum and the coccyx. Anatomy of the cervical spine Typical cervical morphology All seven cervical vertebrae are unique in that they contain the transverse foramen in each transverse process.
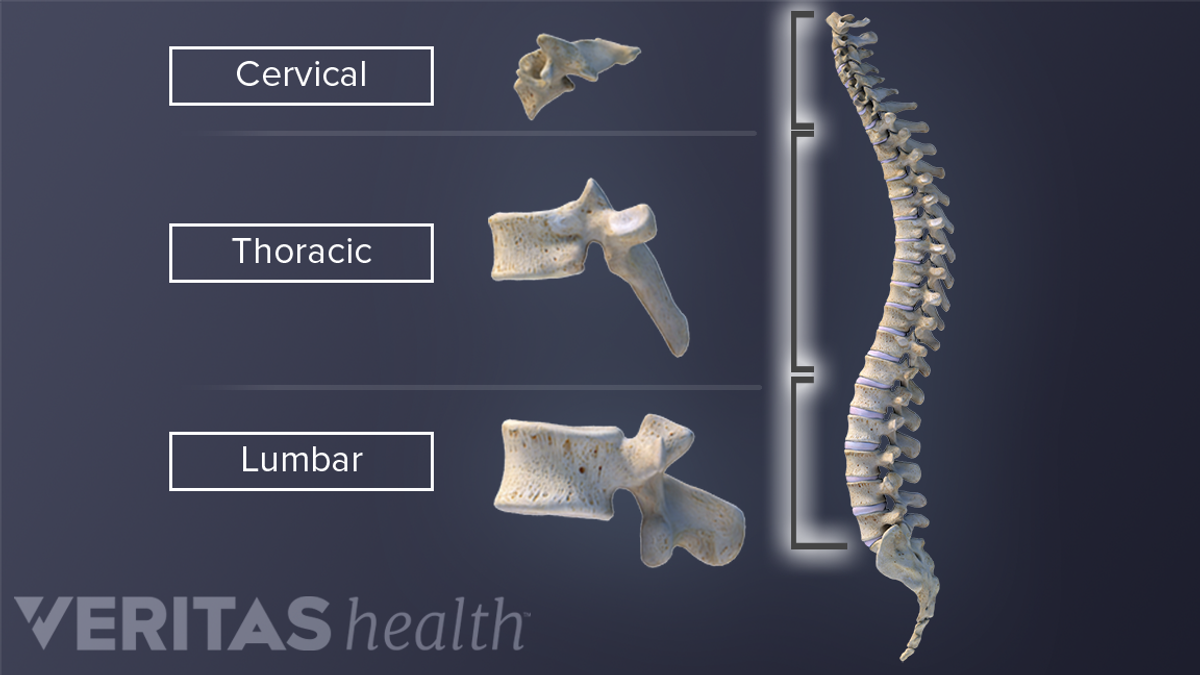
The cervical spine is made up of two anatomically and functionally different segments. There are seven twelve and five articulating vertebrae in the cervical thoracic and. The first thoracic vertebra is designated Thl.
All of the cervical vertebrae flex and extend the neck but some have additional special functions including. The dens is a bony projection found on the first cervical vertebrae. What is the action of the sternocleidomastoid.
According to Panjabi when a load is applied to a spinal functional unit SFU the result is a range of motion ROM which before reaching its maximum passes through a neutral zone and an elastic zoneThe neutral zone is the portion of the intervertebral mobility area closest to the rest position in which the joint has the largest capacity for movement with minimal. With these data cervical spinal motion during direct laryngoscopy and intubation was described in two ways. The motion through the first cervical vertebrae is best described as.
Joint between occiput and C1 primary motion is flexion and extension 15-20 degrees allows little sidebending 5 degrees allows little to no rotation Atlantoaxial Joint AA joint between C1 and C2 primary motion is rotation about 50 of all cervical rotation allows a small amount of flexion and extension 5 degrees very little or no sidebending joint held together by transverse. 1 and 2 c. The atlas is the first cervical vertebra and articulates with the occiput of the head and the axis C2.
Participates is subaxial C2-C7 cervical motion which provides. The first vertebra in the column closest to.

The Atlas Anatomy First Cervical Vertebra C1 Head And Neck Osteology Youtube
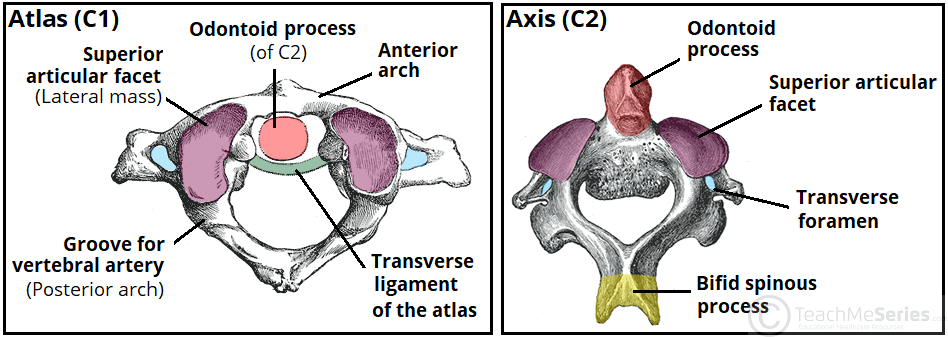
The Cervical Spine Features Joints Ligaments Teachmeanatomy
Introduction To Overview Of The Cervical Spine Of The Neck

Atypical Cervical Vertebrae Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Cervical Vertebrae Physiopedia

Cervical Vertebra Prohealthsys

Spinal Anatomy Vertebral Column
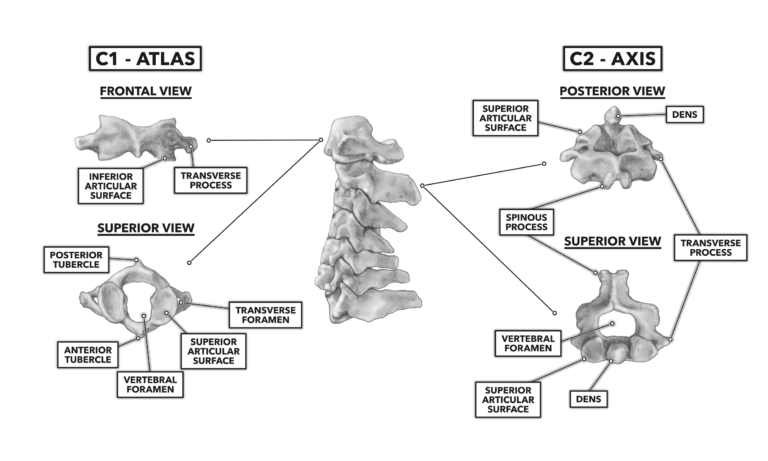
Crossfit The Cervical Vertebrae
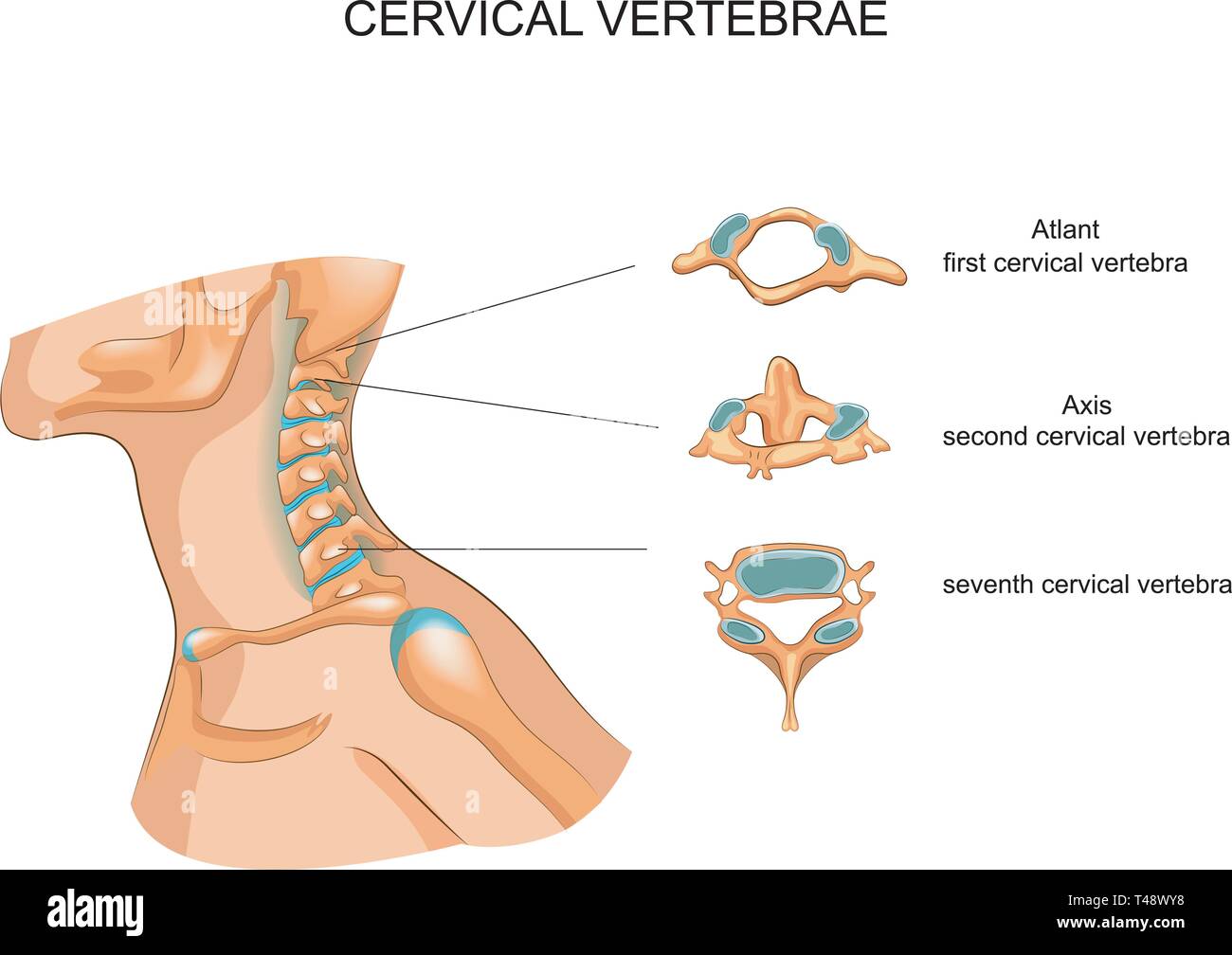
Vector Illustration Of The Structure Of The Cervical Vertebrae Stock Vector Image Art Alamy

First Cervical Vertebra An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cervical Spine Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Cervical Spine Neck What It Is Anatomy Disorders

First Cervical Vertebra An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cervical Vertebrae Physiopedia
Vertebrae In The Vertebral Column

Cervical Vertebrae Physiopedia

First Cervical Vertebra An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Functional Anatomy Of The Cervical Spine Musculoskeletal Key
Comments
Post a Comment